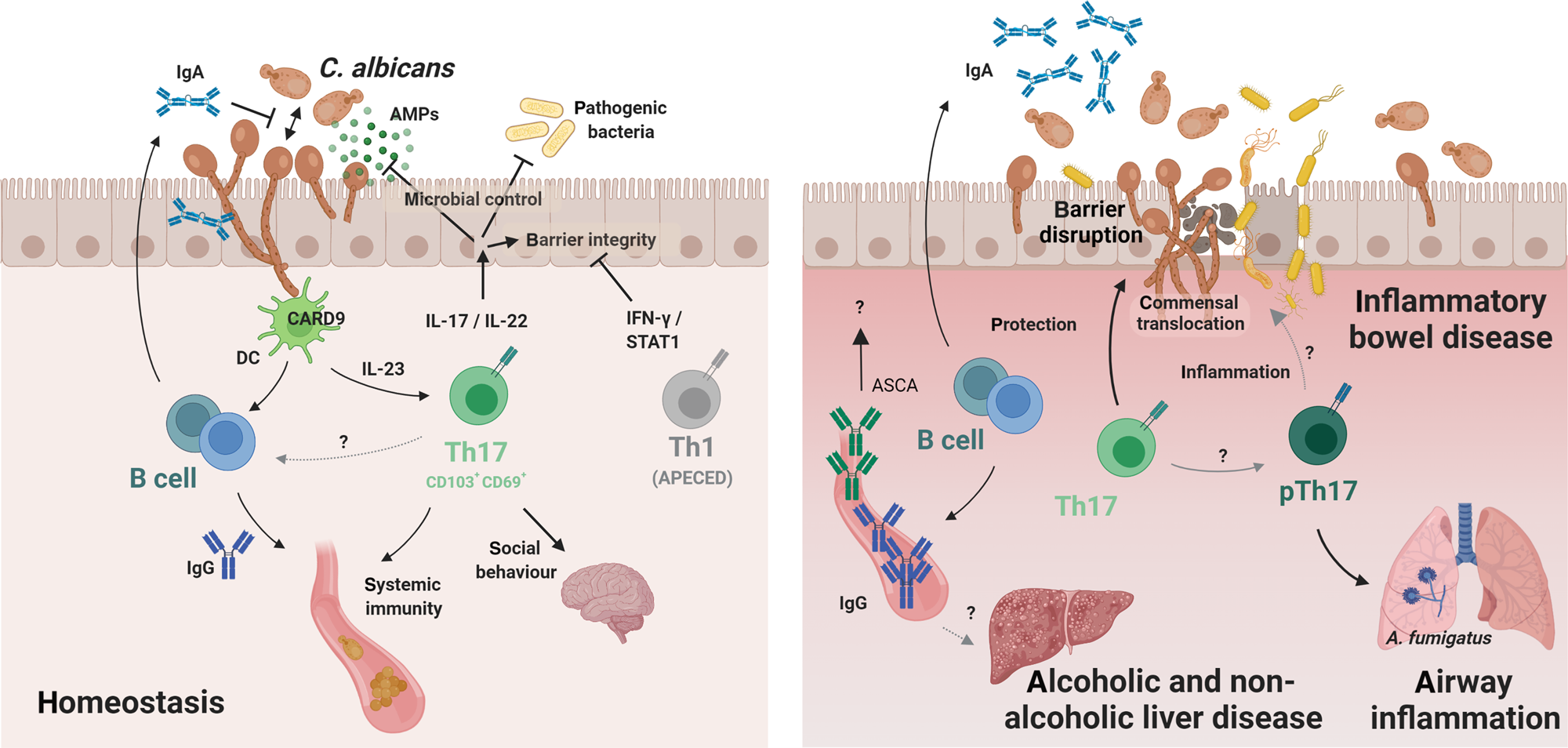
Immunosurveillance of Candida albicans commensalism by the adaptive immune system | Mucosal Immunology

Gastrointestinal colonisation and systemic spread of Candida albicans in mice treated with antibiotics and prednisolone - ScienceDirect
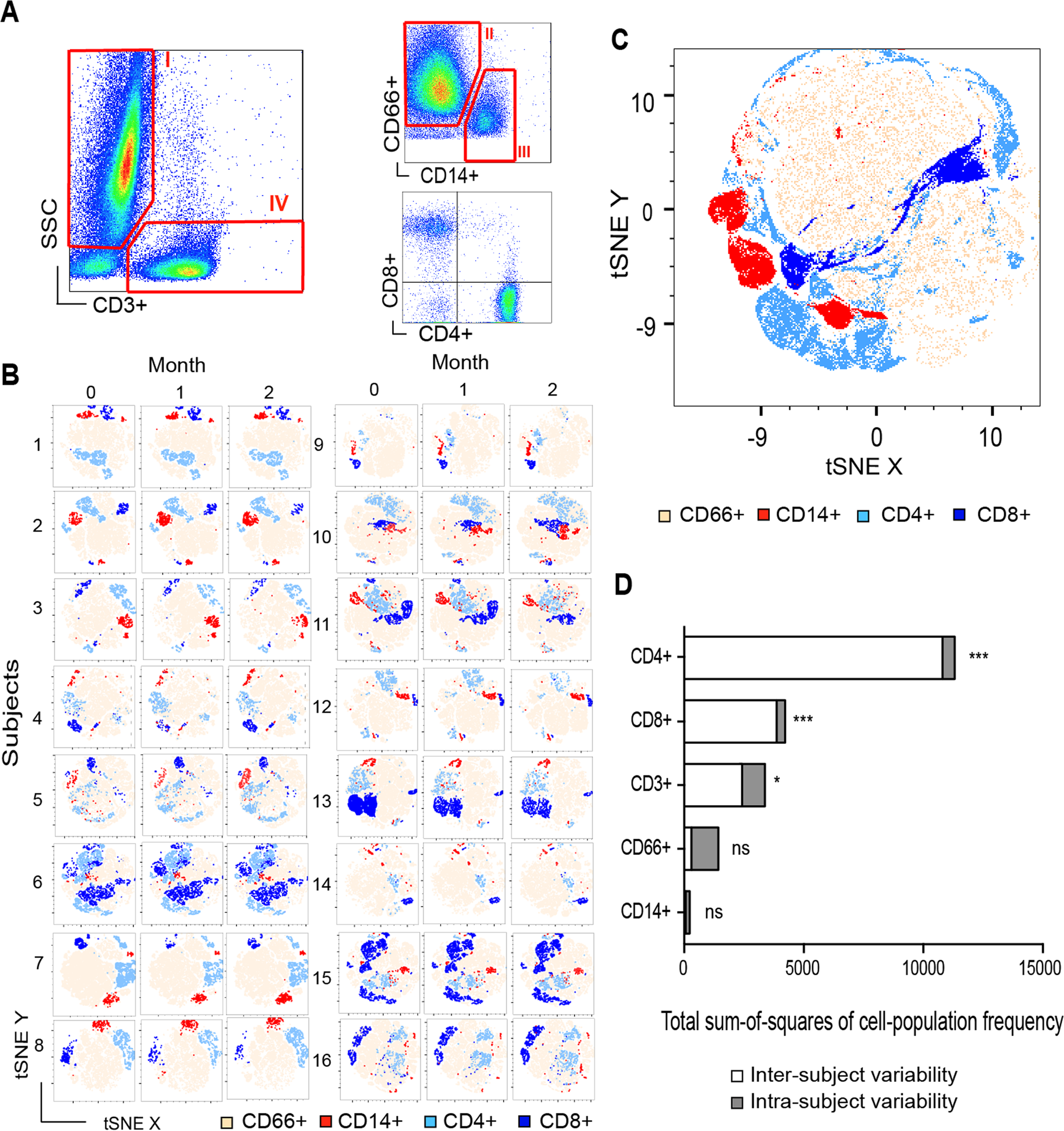
In vitro immune responses of human PBMCs against Candida albicans reveals fungal and leucocyte phenotypes associated with fungal persistence | Scientific Reports

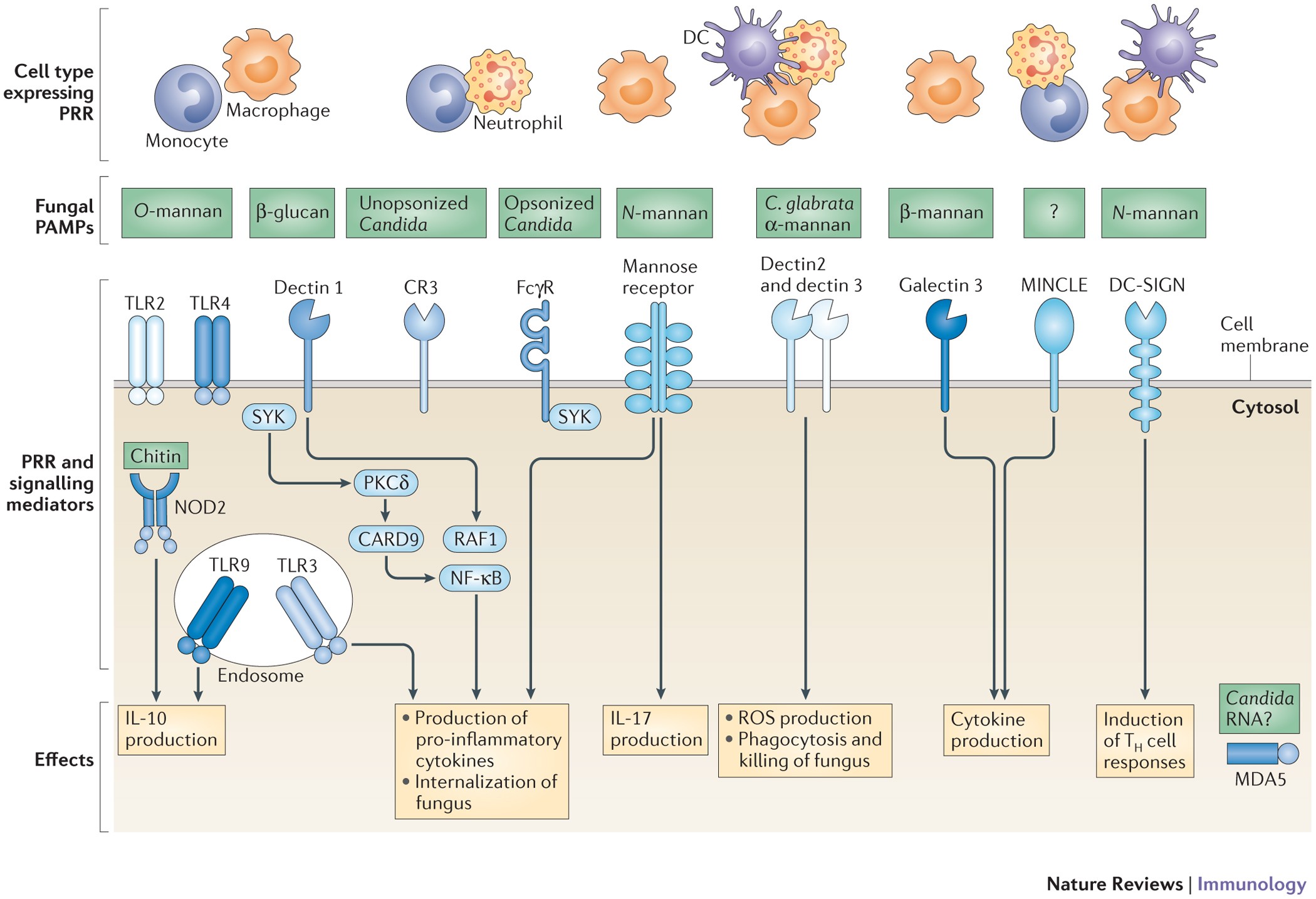
Myeloid cell deficiency of p38γ/p38δ protects against candidiasis and regulates antifungal immunity | EMBO Molecular Medicine

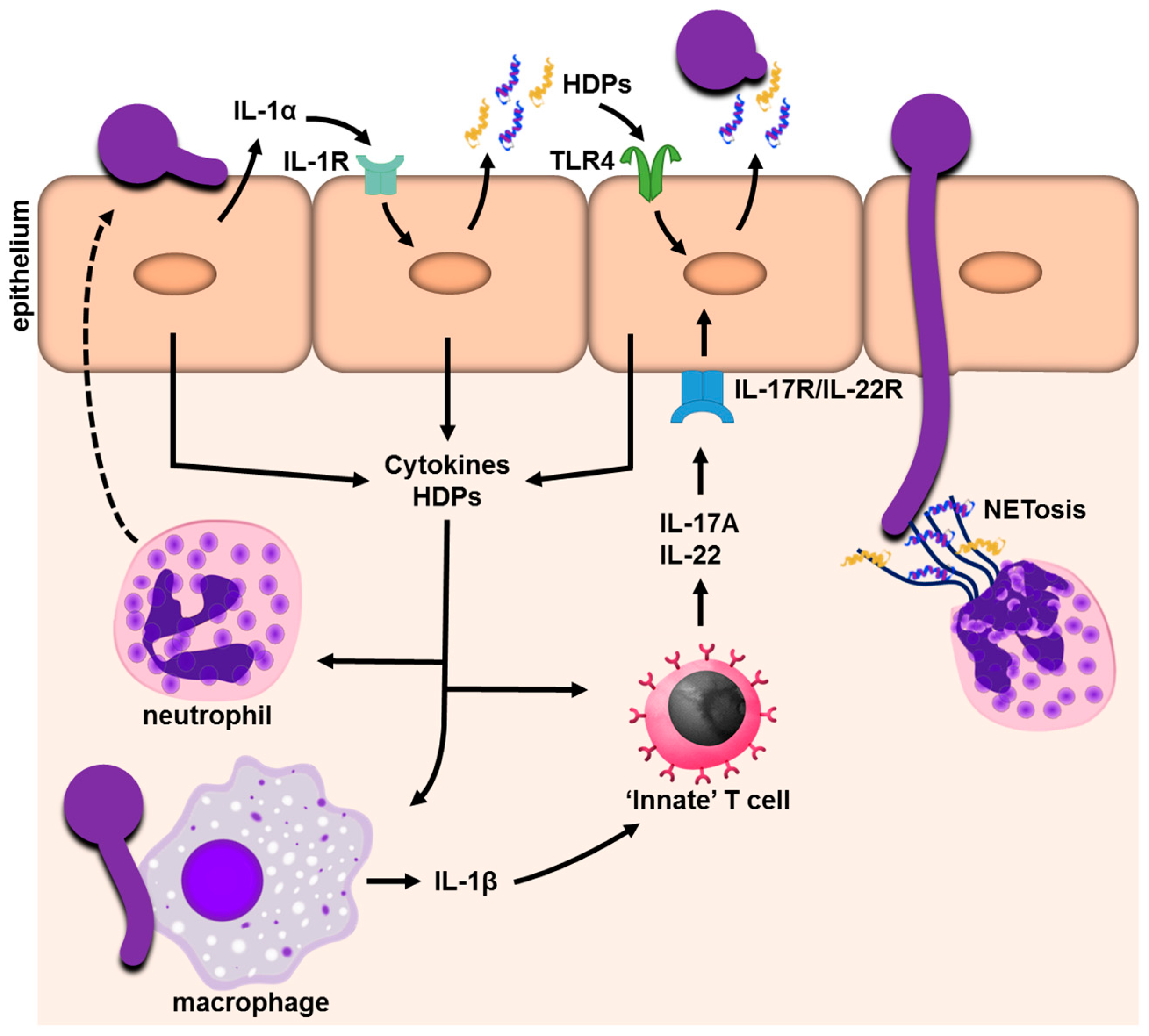
EphA2 Is a Neutrophil Receptor for Candida albicans that Stimulates Antifungal Activity during Oropharyngeal Infection - ScienceDirect
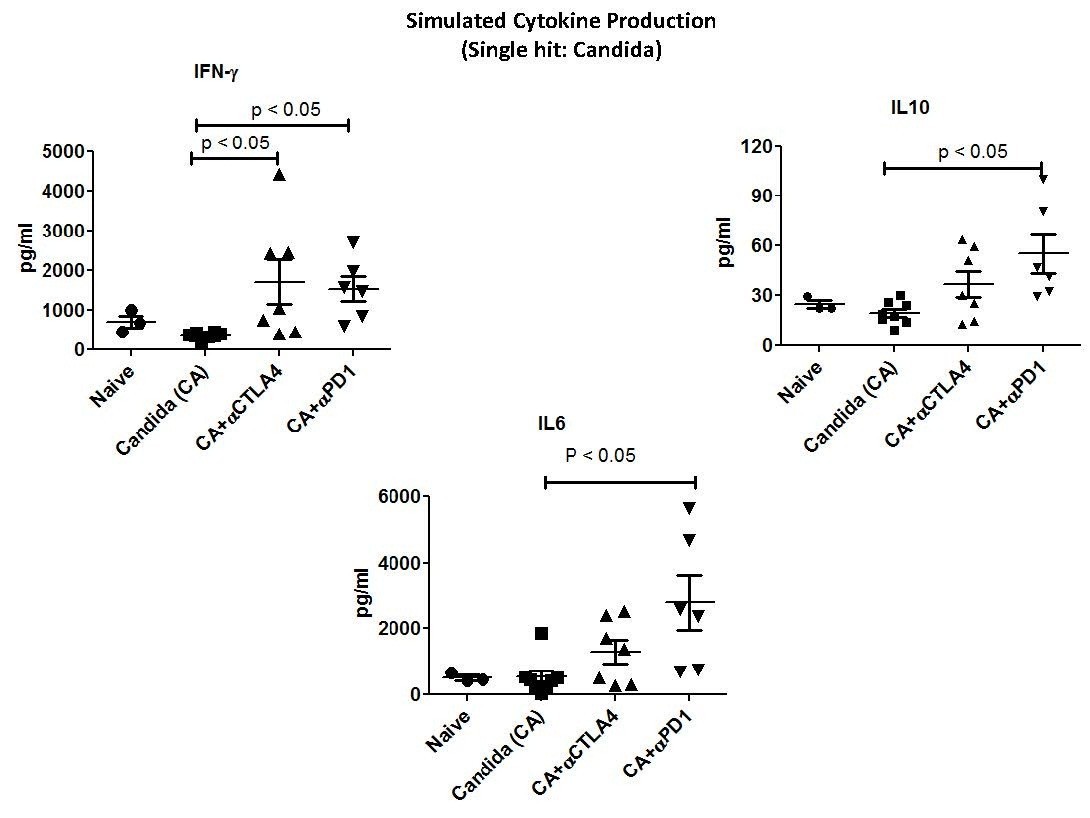
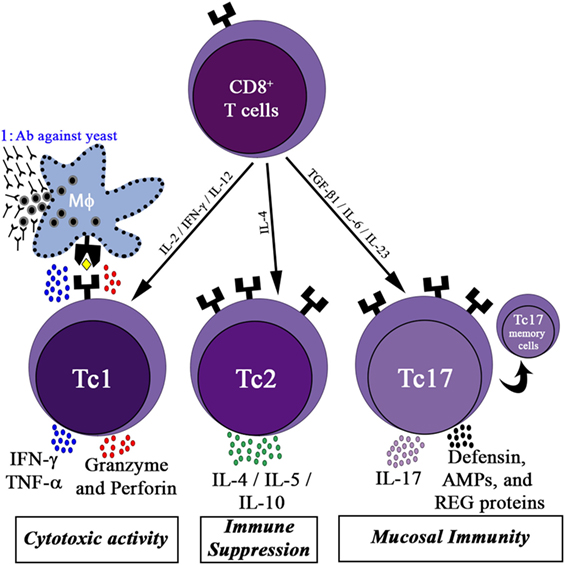
Blockade ofthe negative co-stimulatory molecules PD-1 and CTLA-4 improves survival in primary and secondary fungal sepsis | Critical Care | Full Text
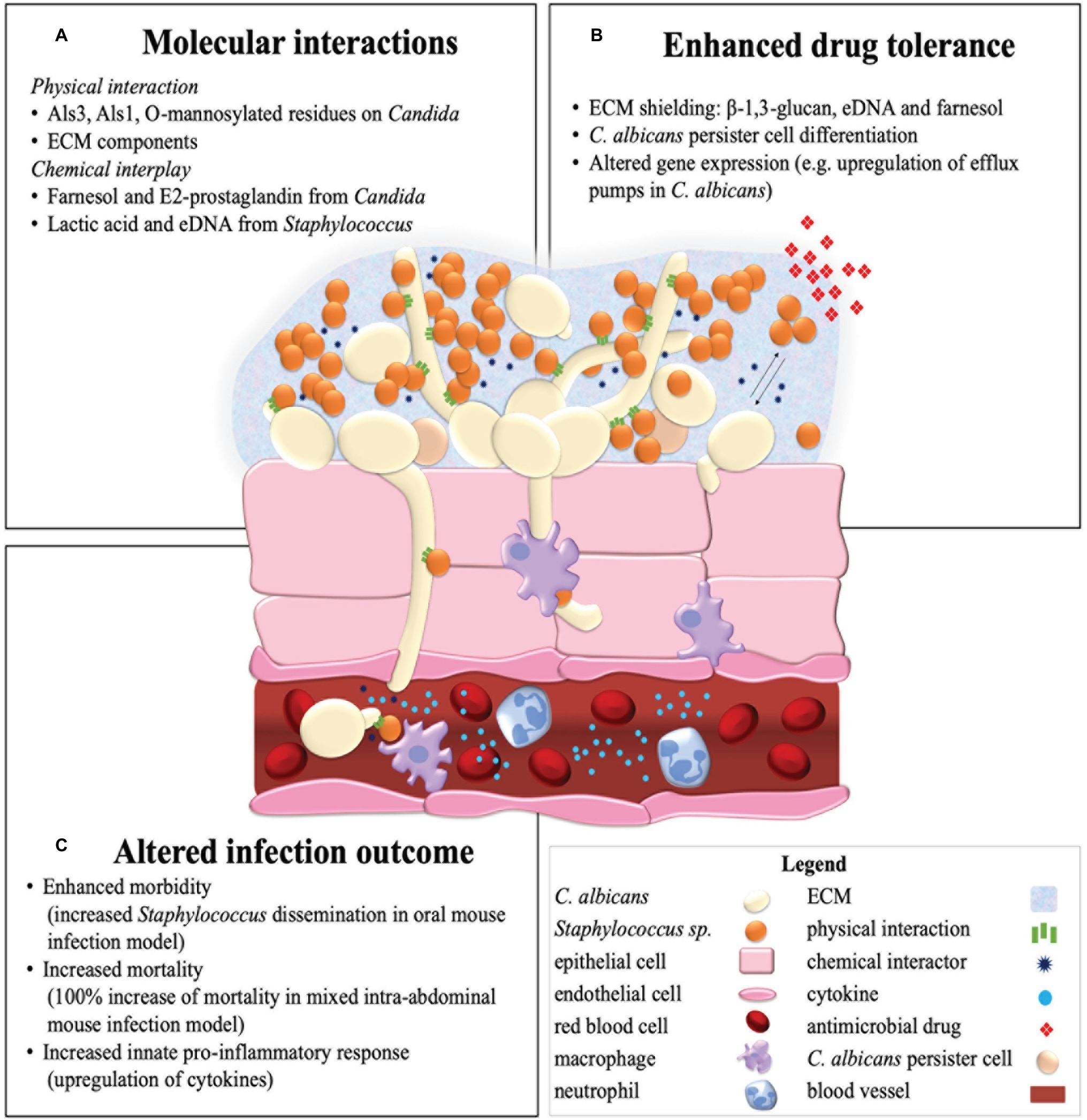
Candida albicans induces mucosal bacterial dysbiosis that promotes invasive infection | PLOS Pathogens
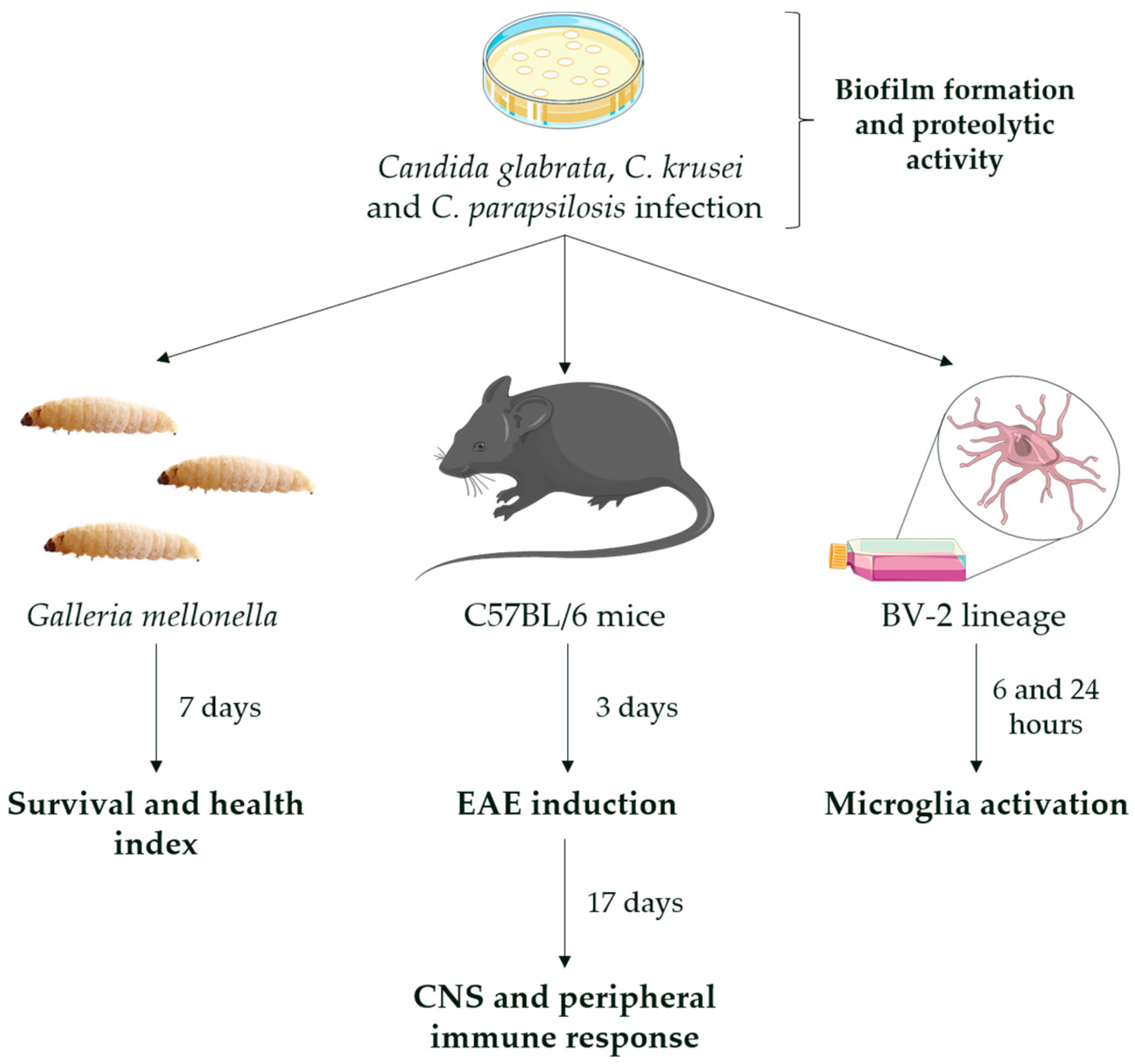
JoF | Free Full-Text | Systemic Infection by Non-albicans Candida Species Affects the Development of a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis

PDF) Increased susceptibility to systemic candidiasis in interleukin-6 deficient mice 1: IL6−/− mice are more susceptible to C. albicans infection
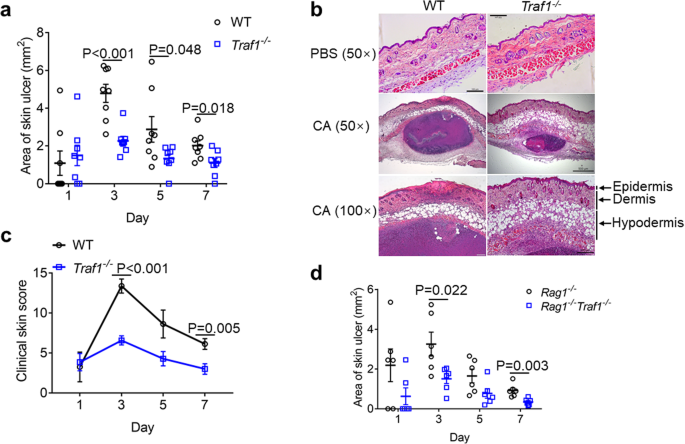
TRAF1 suppresses antifungal immunity through CXCL1-mediated neutrophil recruitment during Candida albicans intradermal infection | Cell Communication and Signaling | Full Text

Myeloid cell deficiency of p38γ/p38δ protects against candidiasis and regulates antifungal immunity | EMBO Molecular Medicine
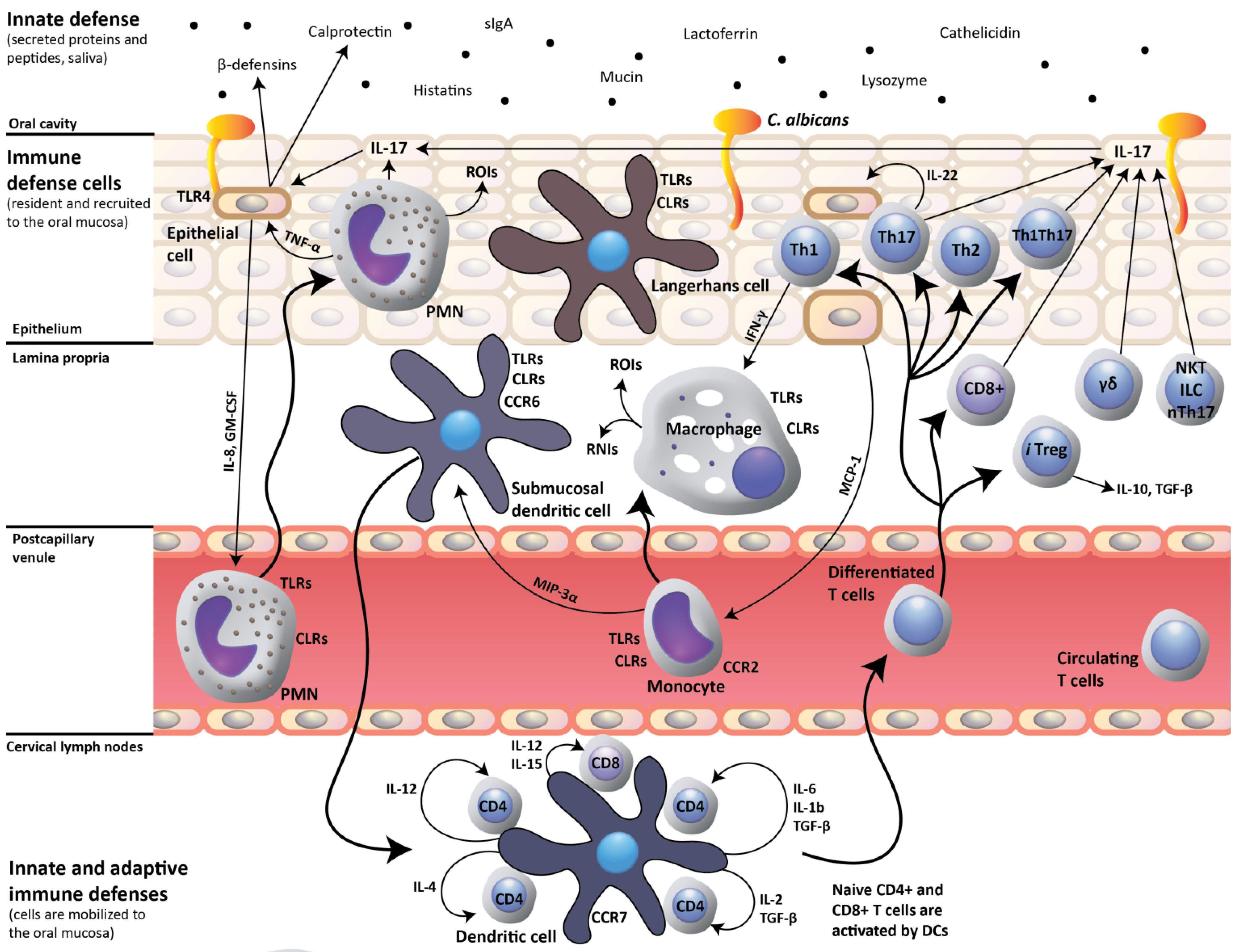
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Oropharyngeal Candidiasis in HIV Infection: Analysis of Impaired Mucosal Immune Response to Candida albicans in Mice Expressing the HIV-1 Transgene

Paeoniflorin augments systemic Candida albicans infection through inhibiting Th1 and Th17 cell expression in a mouse model - ScienceDirect
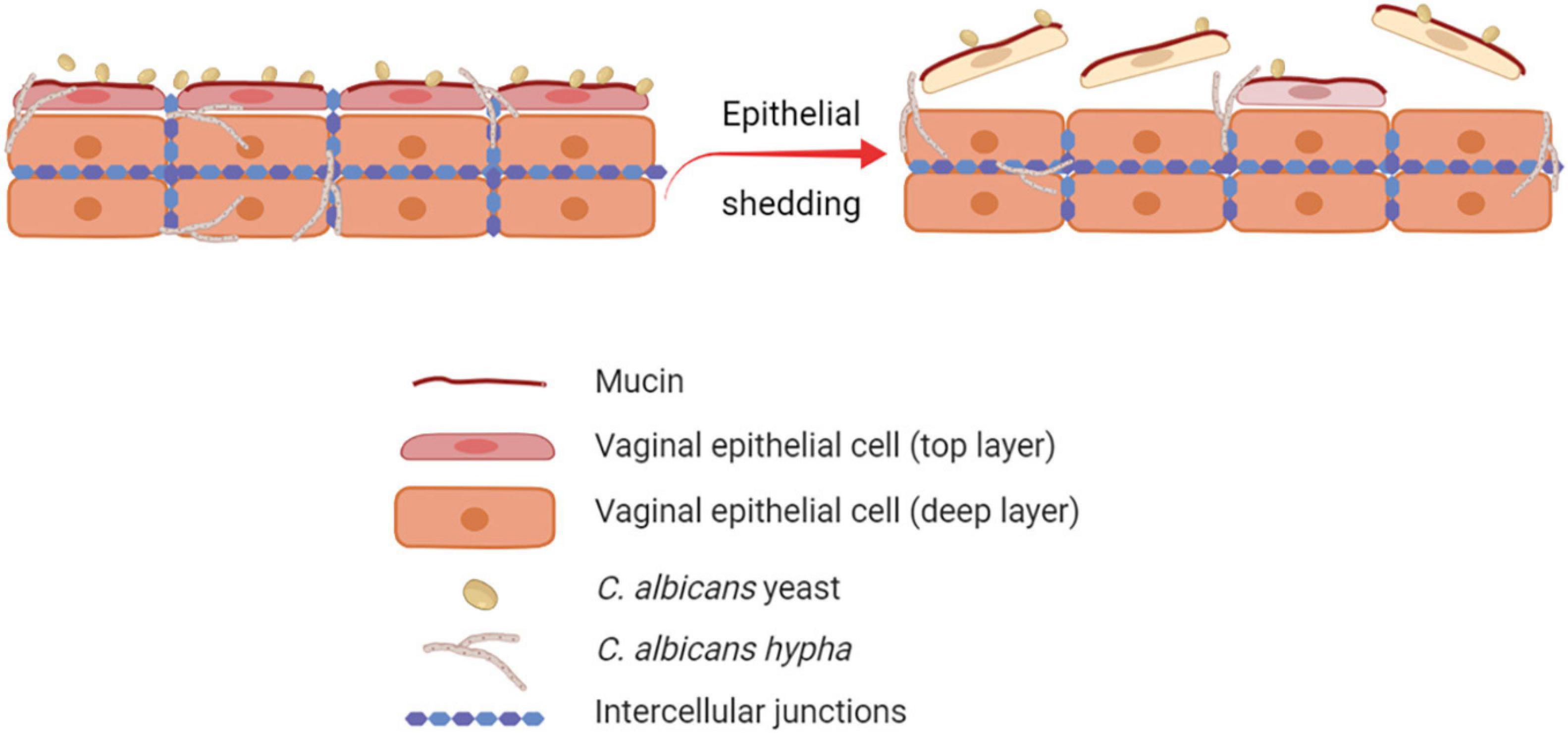
Frontiers | It Takes Two to Tango: How a Dysregulation of the Innate Immunity, Coupled With Candida Virulence, Triggers VVC Onset